- Resources
- News
-
-
Get Email Updates
Sign up for STOP's emails and never miss an update on our latest work and the tobacco industry's activity.
-
Get Funding
Ready to tackle industry interference? You could be eligible for a grant.
-
Share a Tip
Do you have information on tobacco industry misconduct in your country? Let us know.
-
Get Email Updates
Get the full picture on which countries are fighting back, and how.
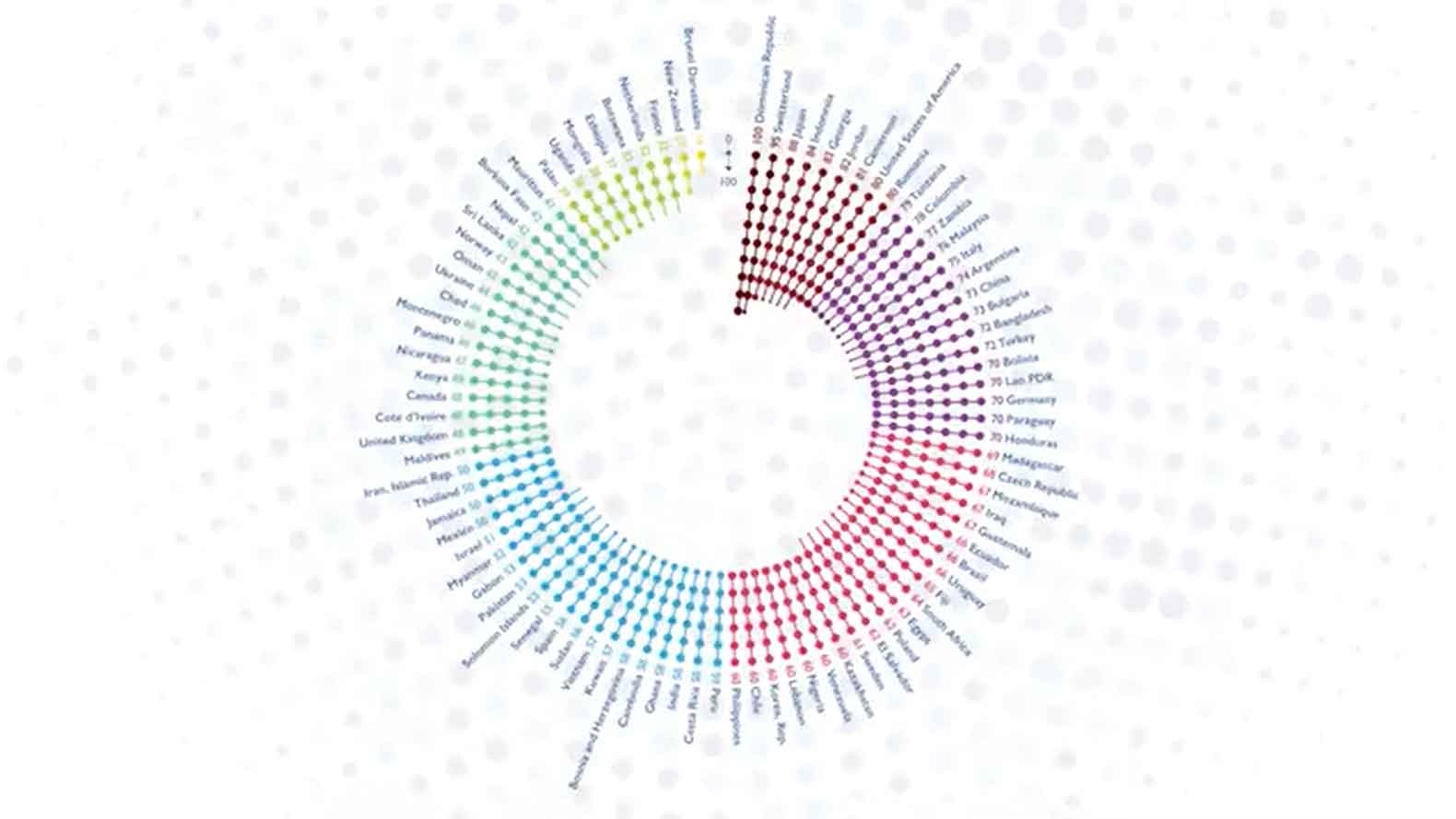
The Global Tobacco Industry Interference Index shows which governments are leading the way in protecting policies from Big Tobacco’s meddling, and which governments can do better.
Global Report

In partnership with

Trends by Region
In Cameroon, British American Tobacco was actively involved in developing the standards for its Velo and Vuse products, and provided financial support for the work. In Ethiopia, while the country privatized its state-owned tobacco enterprise, the law allows the industry to comment on tobacco control measures. In Kenya, British American Tobacco announced that it had agreed with the Ministry of Health about reversing a ban on nicotine pouches.
Tanzania’s Prime Minister advocated to increase tobacco farming and secure more markets, with the Minister of Agriculture committing to doubling tobacco production. In Madagascar, the government provided a 2% tax rebate for cigarettes manufactured with 70% or more locally produced tobacco. In Kenya, the Cabinet Secretary for Health was the chief guest at a breakfast roundtable meeting hosted by the National Chamber of Commerce and Industry for which British American Tobacco Kenya was a main sponsor.
In Sweden, members of the parliament attended the greenwashing campaign, “Håll Sverige Rent” (Keep Sweden Clean), of an NGO funded by Philip Morris International and other tobacco companies. In Switzerland, the Federal Office for the Environment formed a partnership with the main tobacco companies and launched a nationwide awareness campaign addressing cigarette littering. Their public message included: “Dispose of cigarette butts correctly because nature is not an ashtray,” a slogan lifted from a past Swiss Cigarette CSR campaign.
The General Police Headquarters of Poland organized a training by British American Tobacco Poland and the eSmoking Institute in Poznań associated with the company on counteracting smuggling of tobacco products. Georgian State Customs received training through a series of anti-illicit trade seminars conducted by Japan Tobacco International. In Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Administration of Indirect Taxation is implementing the “Stop the Smuggling” campaign in collaboration with the Association of Economists SWOT, which is supported by Philip Morris International, British American Tobacco and Japan Tobacco International.
In Korea, the local government of Suwon City endorsed KT&G to set up 33 cigarette butt bins in 23 public facilities and promoted the company’s “Sseudam Sseudam” (cigarette butts in the trash) campaign. Forestry Departments in Pakistan and Sri Lanka endorsed tree planting programs sponsored by local British American Tobacco subsidiaries. The mayor or Bangladesh’s Khulna City Corporation inaugurated the tree plantation “Bonayon” project sponsored by British American Tobacco.
In Lao PDR, the tobacco industry is not fully compliant in applying the 75%-size warnings on all its cigarette packs. In Myanmar, transnational tobacco companies and local cigarette and cheroot producers successfully lobbied for the standardized tobacco packaging implementation deadline to be pushed back. In Bangladesh, the implementation of pictorial health warnings (PHW) to be applied to the upper half of tobacco packs has been delayed since the High Court postponed the government order from 2017, following a further petition by the Bangladesh Cigarette Manufacturers’ Association.
In 2021 in Brazil, the industry used the Tobacco Sectorial Chamber to lobby the Ministry of Foreign Affairs to guide the intervention of Brazil during the ninth Conference of the Parties (COP9) negotiations. Through two unregistered meetings, it lobbied the government, with the Minister of Agriculture assuring the industry it would support tobacco producers during COP9. In Colombia, attempts to regulate industry lobbying have not been successful because, although the Anti-Corruption Statute may request information on lobbyists, it does not have specific reference to nor registration for tobacco industry entities.
In Argentina, the tobacco industry has links with different levels of government on child labor issues through the Fundación Vamos Andar-Programa Brazos Abiertos. At the national level, this organization coordinated British American Tobacco Argentina’s sponsored activities on child labor with the National Registry of Rural Workers and the National Secretariat for Children, Adolescents and Family of the Nation. In Brazil, the Ministry of Labour supports the “Growing Up Right” Institute, a project by Sinditabaco and its associated companies (including British American Tobacco Brasil, Philip Morris Brazil, Japan Tobacco International and Alliance One), which claims to promote education and fight child labor in rural areas.
In Iraq, the Minister of Industry visited Baghdad Tobacco Factory to express support for the tobacco business. In Lebanon, a representative of the British High Commission attended the inauguration of a new production line of the Lebanese state-owned tobacco monopoly, Regie, which was also attended by representatives of international tobacco companies.
In November 2022, Iran’s Vice President of Commerce and Economy promoted Iran Tobacco Company (ITC), a state-owned enterprise, through an agreement with Zimbabwe. The increase in tobacco investment was discussed during a visit led by Zimbabwe’s First Lady to Tehran. Two months later, ITC’s CEO and Zimbabwe’s Agriculture Minister signed an agreement for Zimbabwe to supply tobacco for cigarette manufacturing in Iran or for re-exports to Central Asia. In Iraq, the government provided various levels of support to the national tobacco industry, including tax exemptions and financial facilities.
Issues
Without full implementation of Article 5.3 of the WHO FCTC, which aims to protect public policies from the influence of the tobacco industry, the industry is able to target departments friendly to its business, partner with governments on social programs that improve its reputation and apply influence outside of the public eye.
The tobacco industry has increasingly gone around ministries of health to other departments that may be more friendly to its business interests. The latest Index shows that the industry primarily targeted departments of finance, customs, commerce and investment. In some countries, these departments were persuaded by the industry’s exaggerated claims that increased tobacco taxes would worsen illicit trade.
Many governments either partnered with the industry or endorsed its “corporate social responsibility” activities around environmental issues. These included efforts to plant trees and clean up cigarette butt litter. Ultimately, these CSR activities distract from the many serious harms the tobacco industry causes to people and the environment.
Many countries still do not have comprehensive, whole-of-government policies in place to reduce unnecessary interaction with the industry, and to record all interactions between government officials and the industry. The result is that tobacco companies can lobby or directly influence policies without the public knowing.
See how your country is ranked:
Don’t see your country?
Check back in 2025 to see if your country was evaluated by our civil society collaborators.
Brunei Darussalam
Overall Score: 14
New Zealand
Overall Score: 27
France
Overall Score: 32
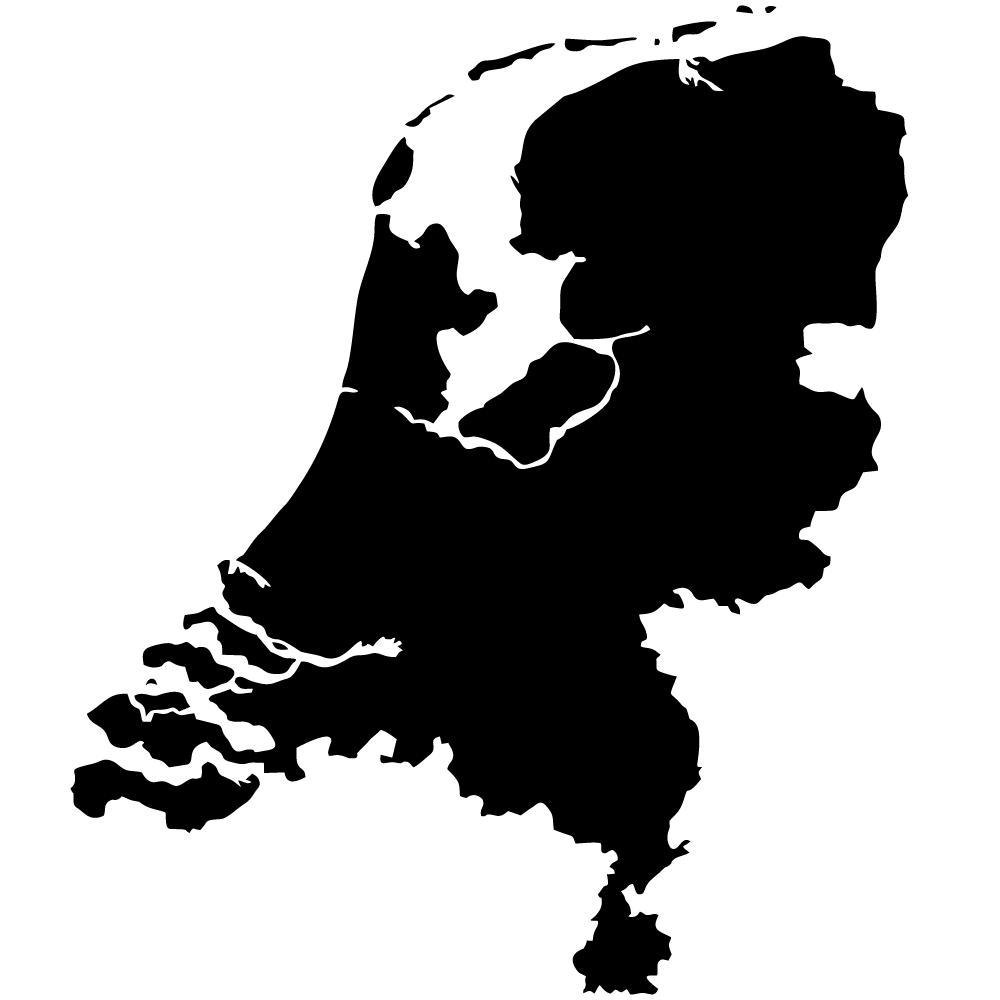

Netherlands
Overall Score: 32
Botswana
Overall Score: 33
Ethiopia
Overall Score: 37
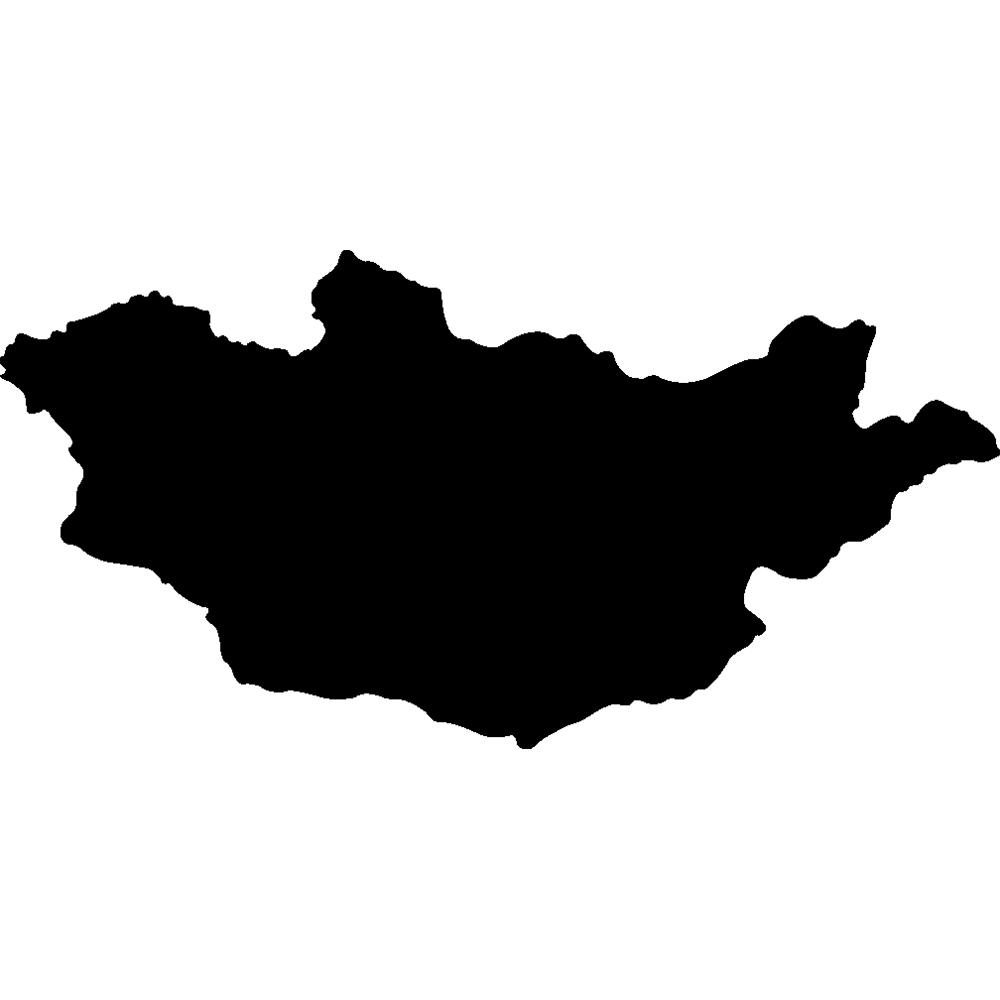

Mongolia
Overall Score: 38
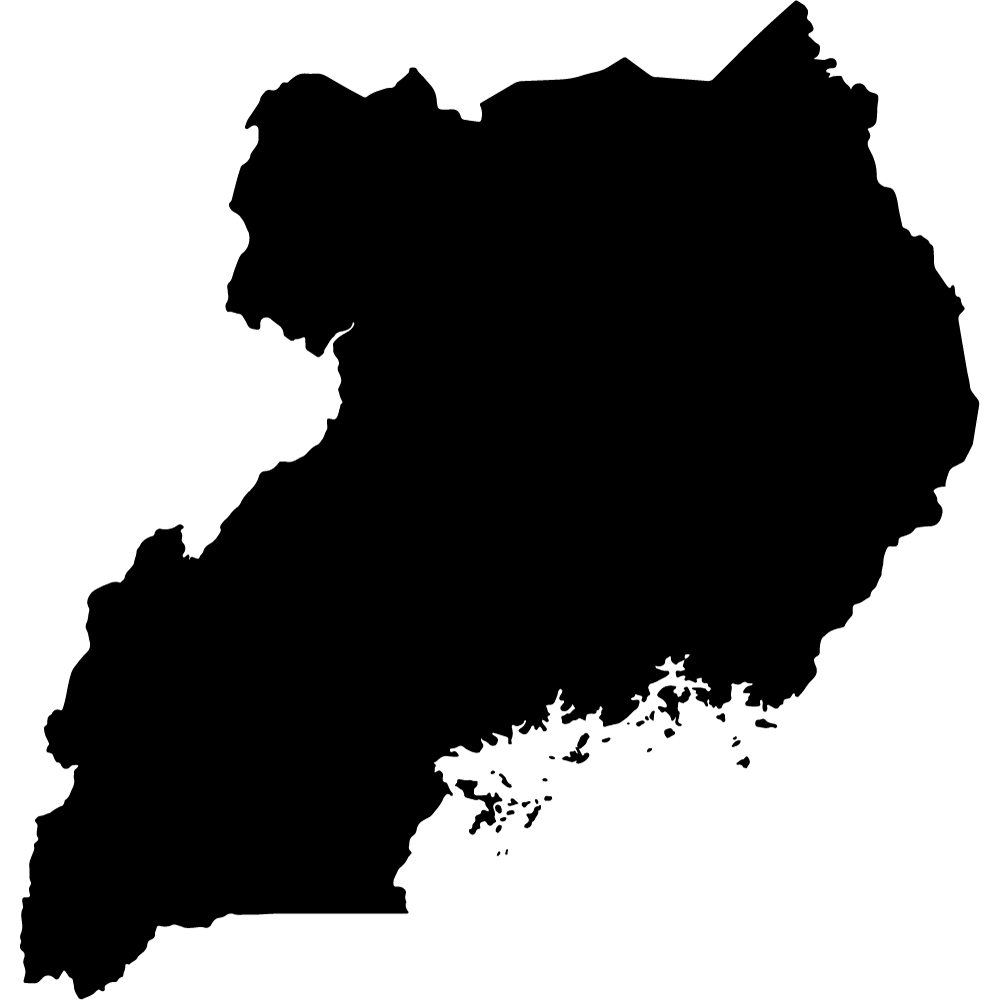
Uganda
Overall Score: 38

Palau
Overall Score: 39

Mauritius
Overall Score: 41
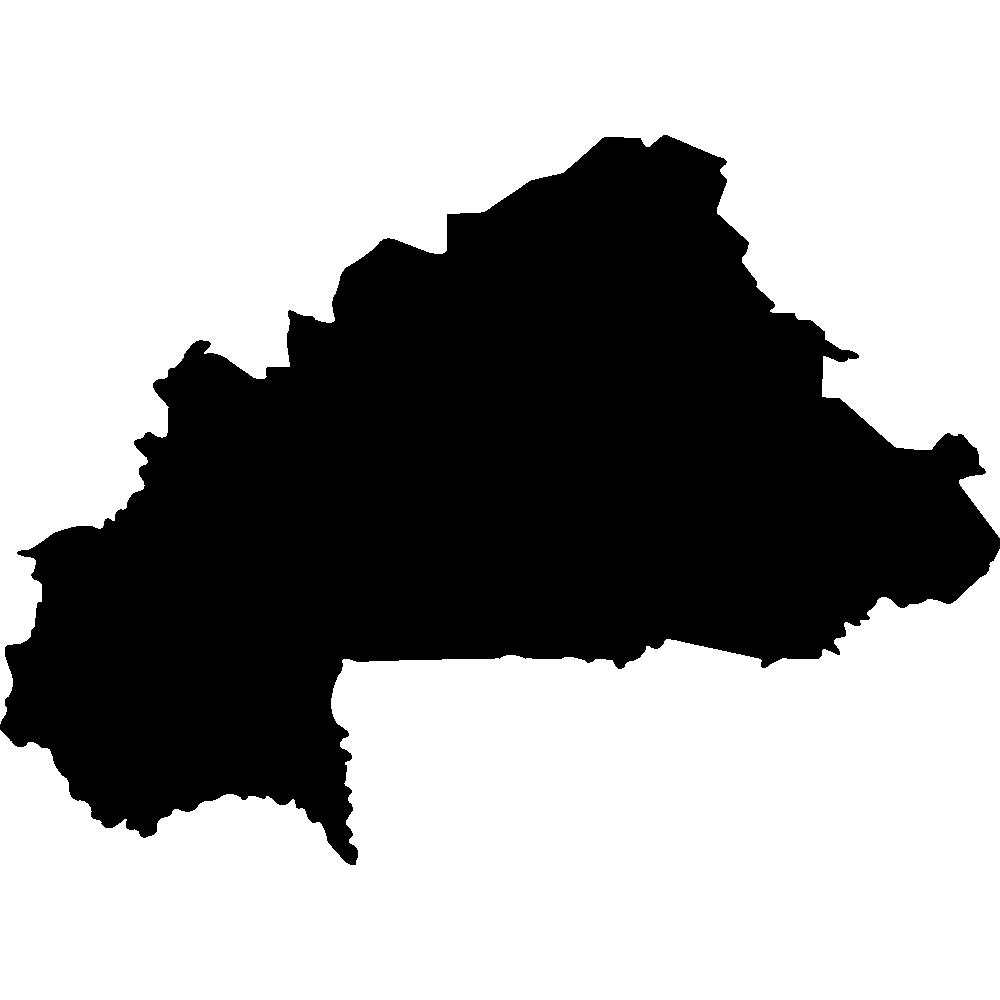
Burkina Faso
Overall Score: 42

Nepal
Overall Score: 42

Sri Lanka
Overall Score: 42

Norway
Overall Score: 43

Oman
Overall Score: 43
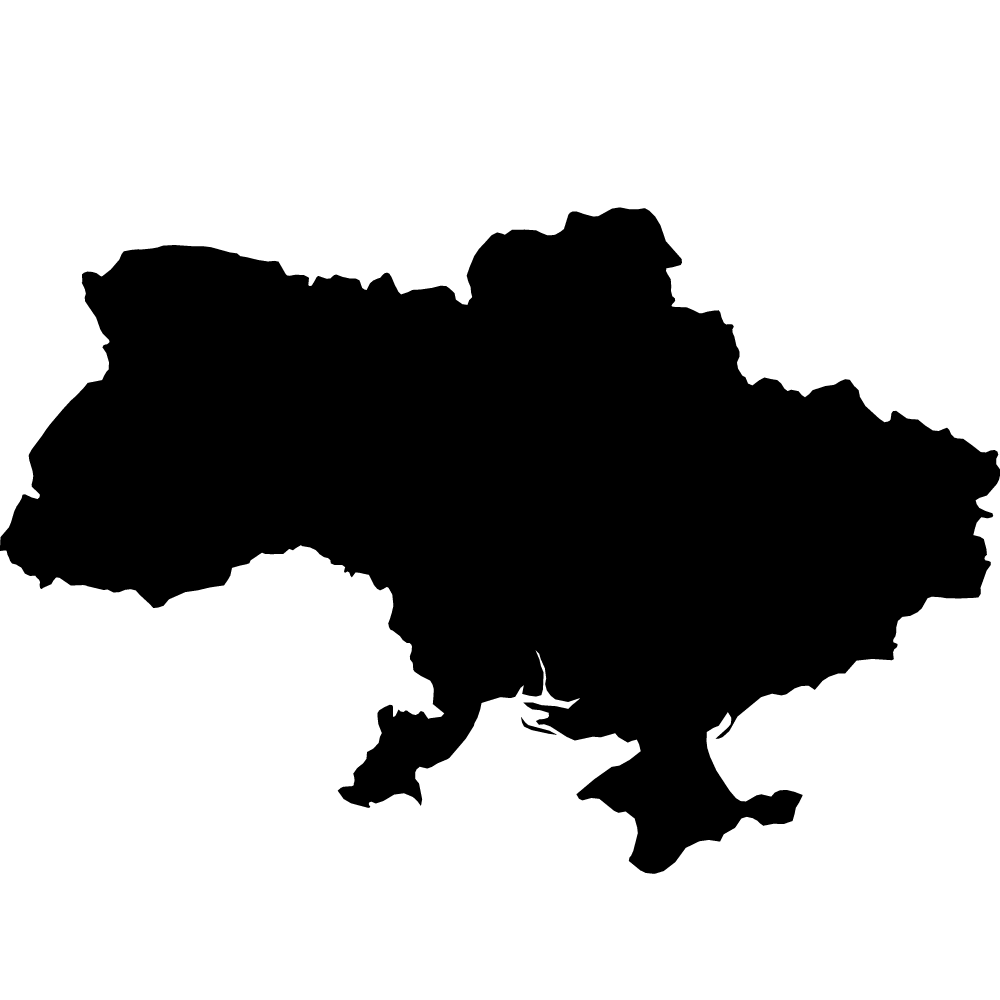
Ukraine
Overall Score: 44

Chad
Overall Score: 46
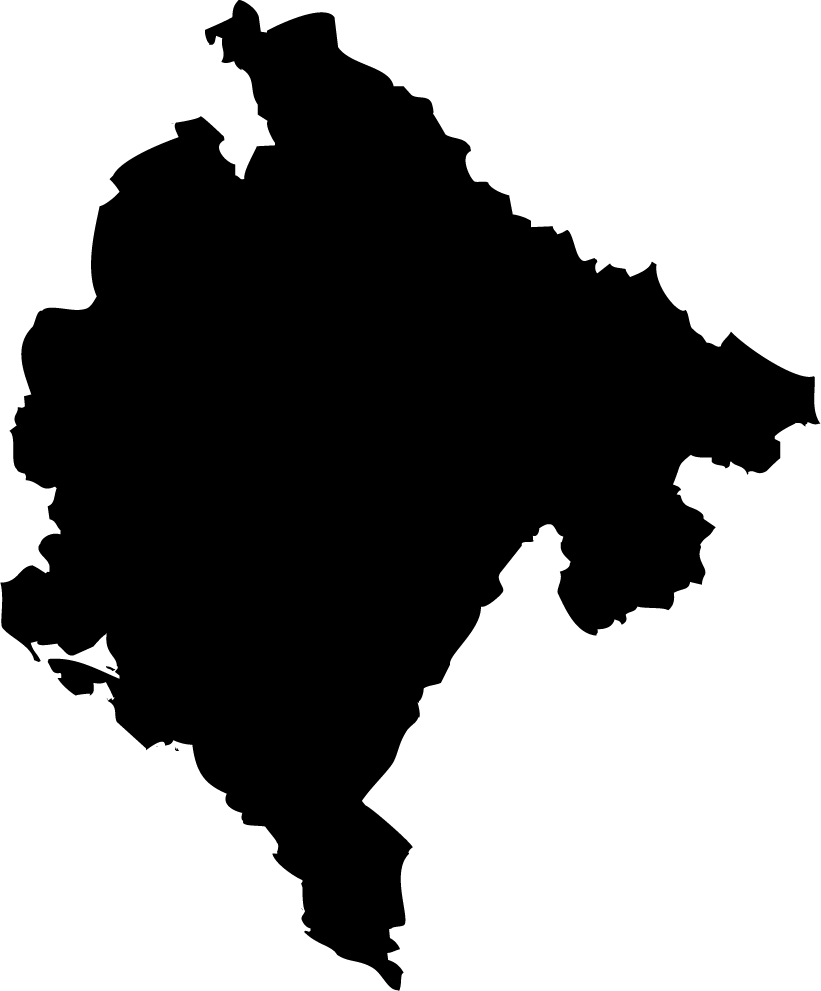
Montenegro
Overall Score: 46

Panama
Overall Score: 46
Nicaragua
Overall Score: 47
Canada
Overall Score: 48
Côte d'Ivoire
Overall Score: 48
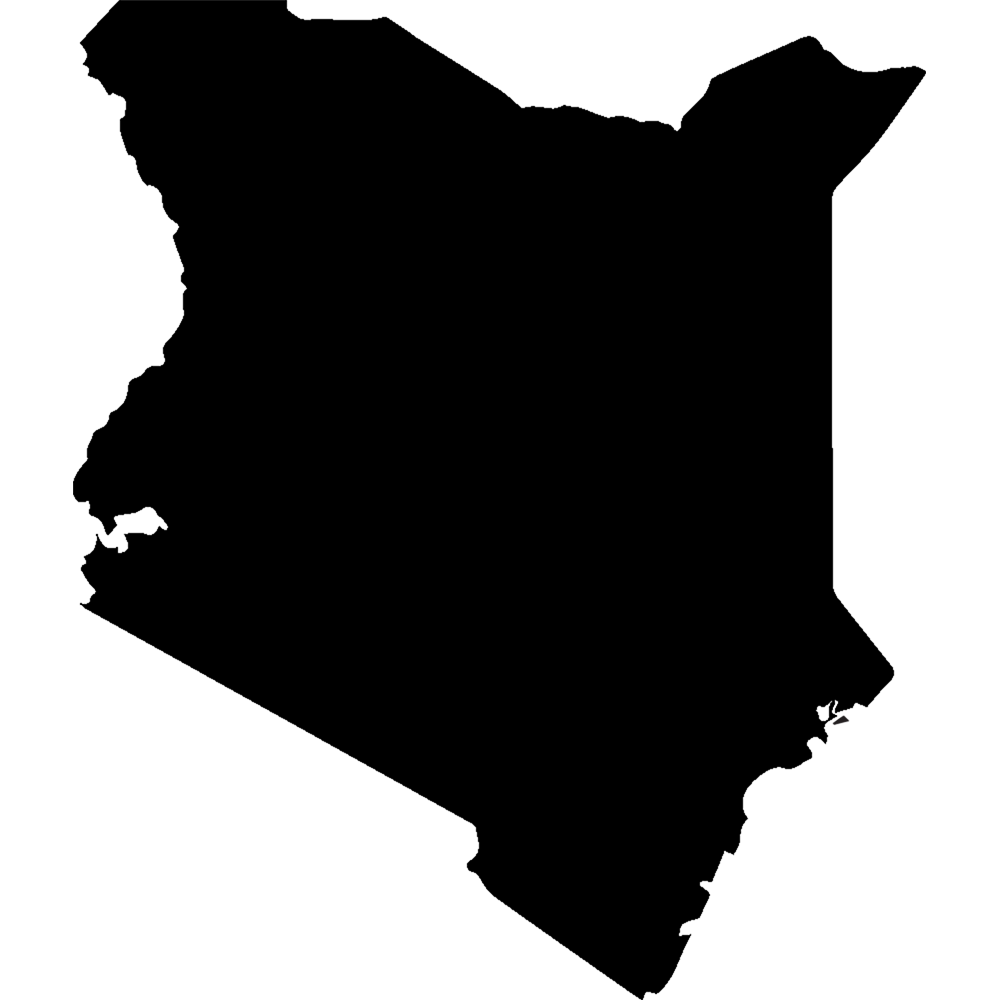

Kenya
Overall Score: 48
United Kingdom
Overall Score: 48

Maldives
Overall Score: 49
Islamic Republic of Iran
Overall Score: 50
Jamaica
Overall Score: 50
Mexico
Overall Score: 50
Thailand
Overall Score: 50
Israel
Overall Score: 51
Myanmar
Overall Score: 52
Gabon
Overall Score: 53
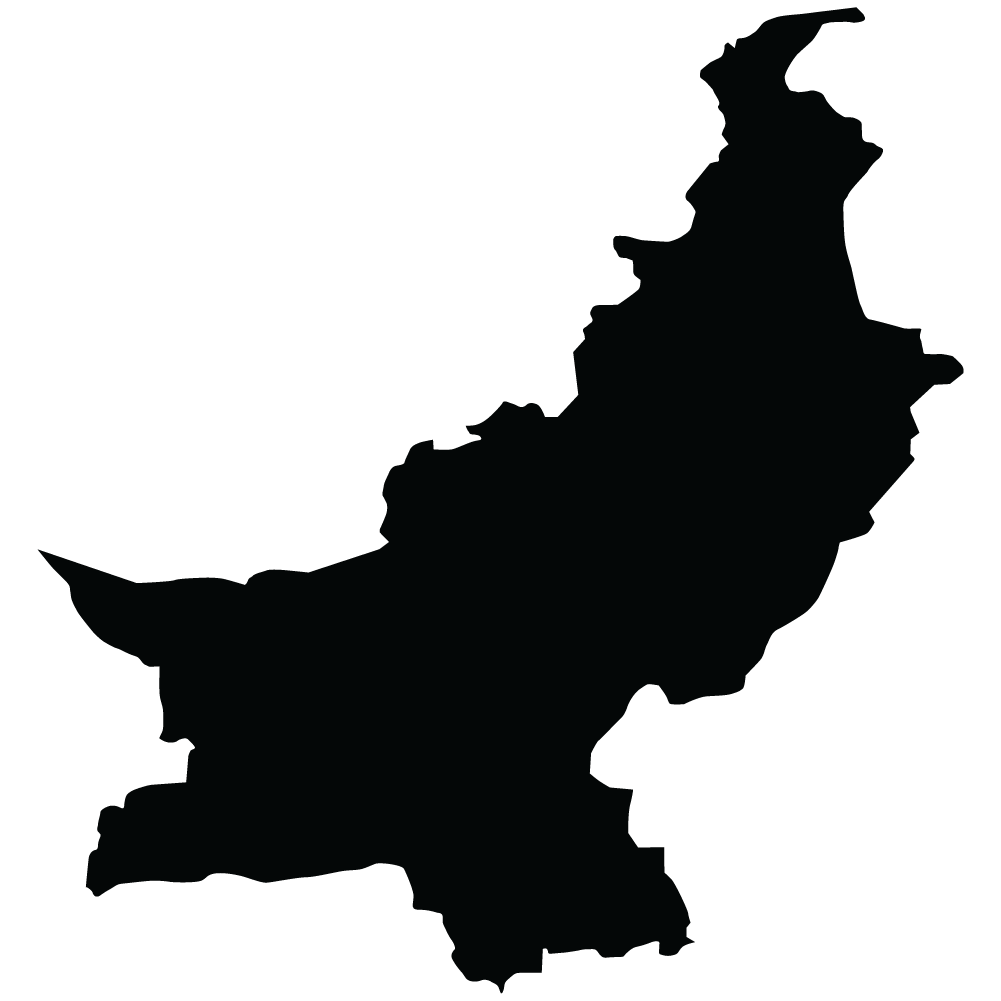

Pakistan
Overall Score: 53

Solomon Islands
Overall Score: 53
Senegal
Overall Score: 55
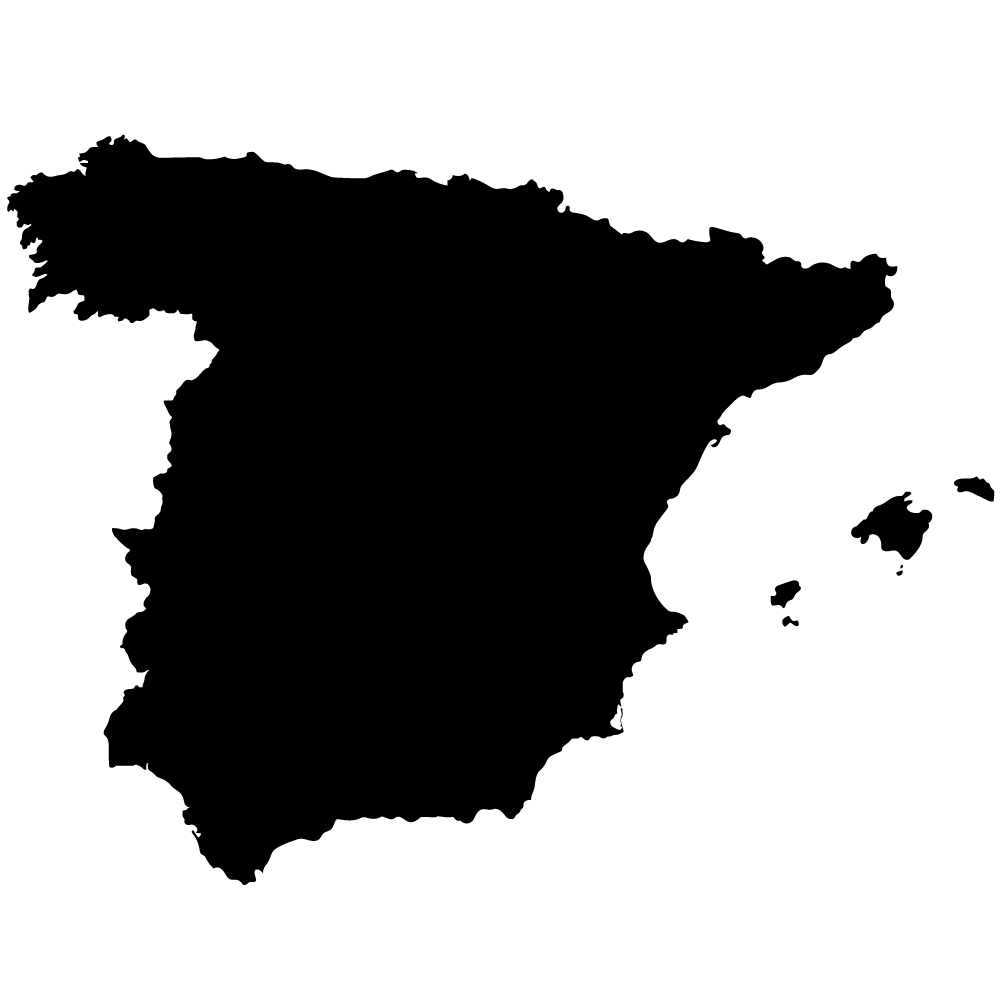
Spain
Overall Score: 56
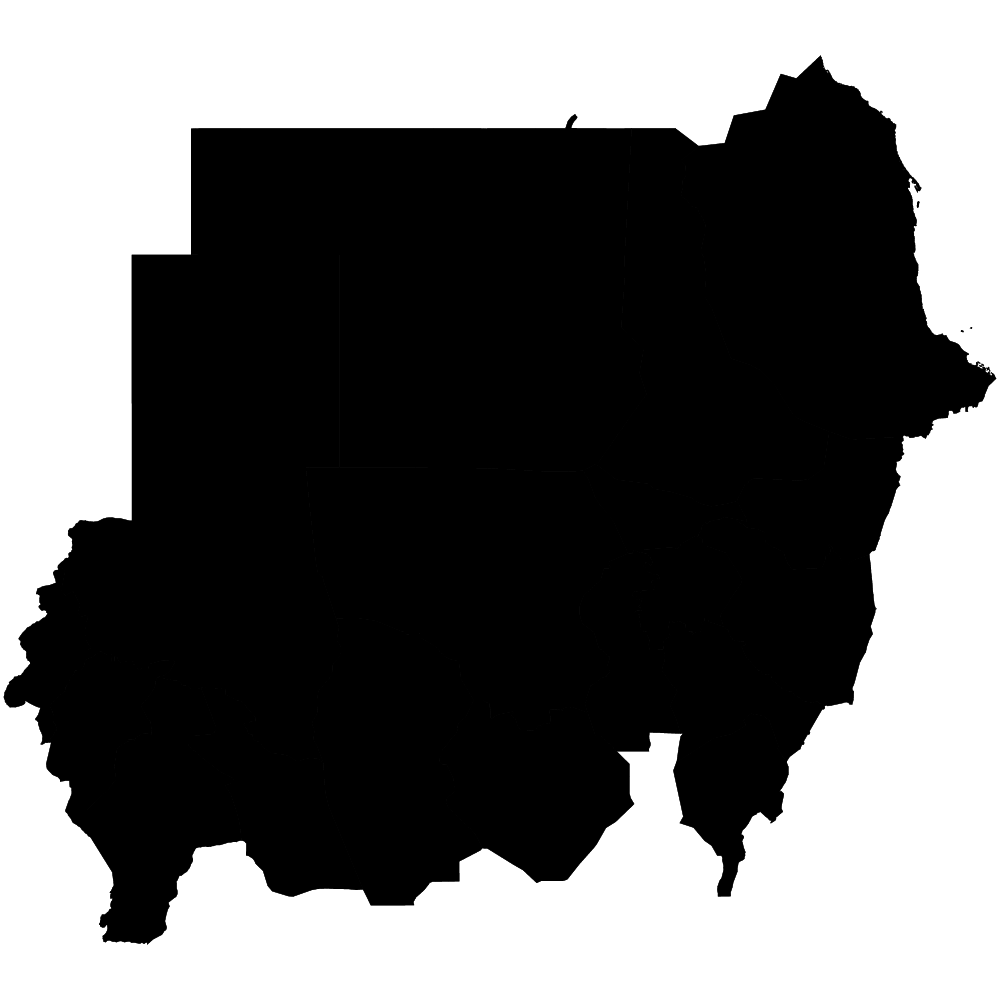
Sudan
Overall Score: 56

Kuwait
Overall Score: 57
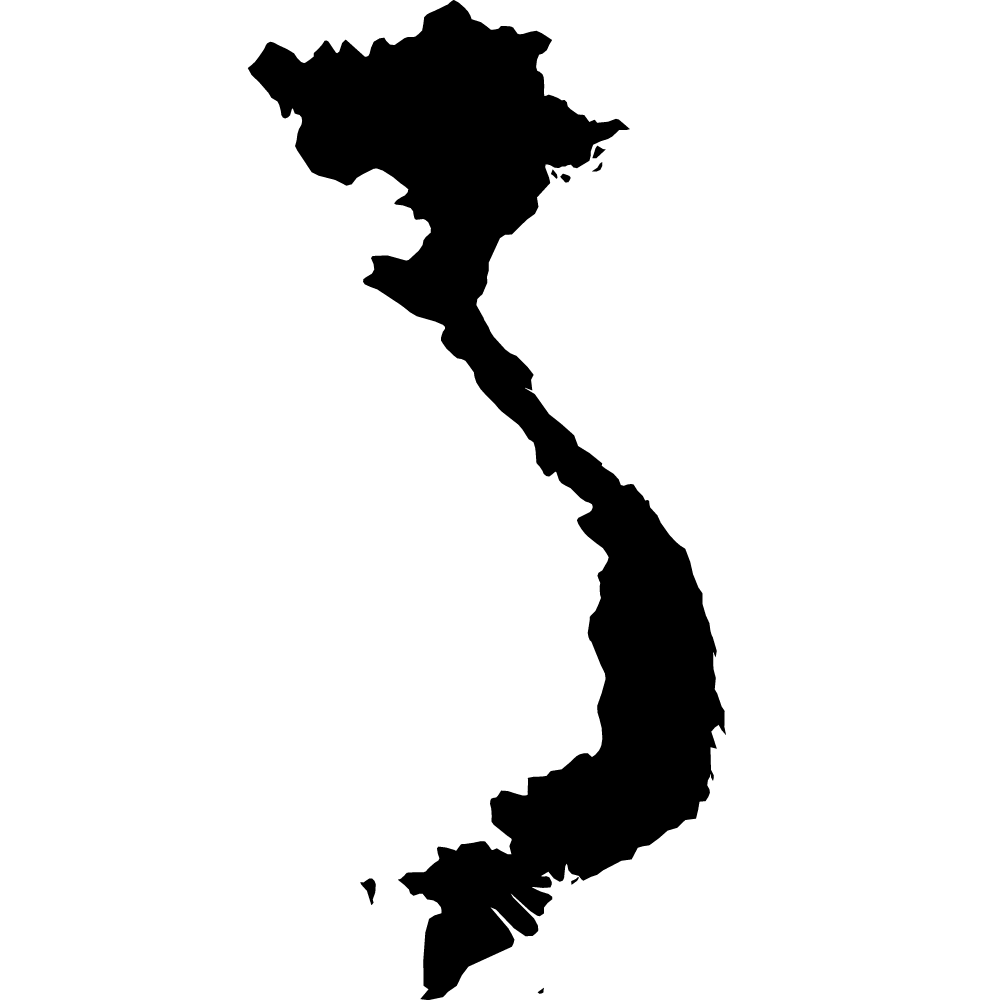
Vietnam
Overall Score: 57
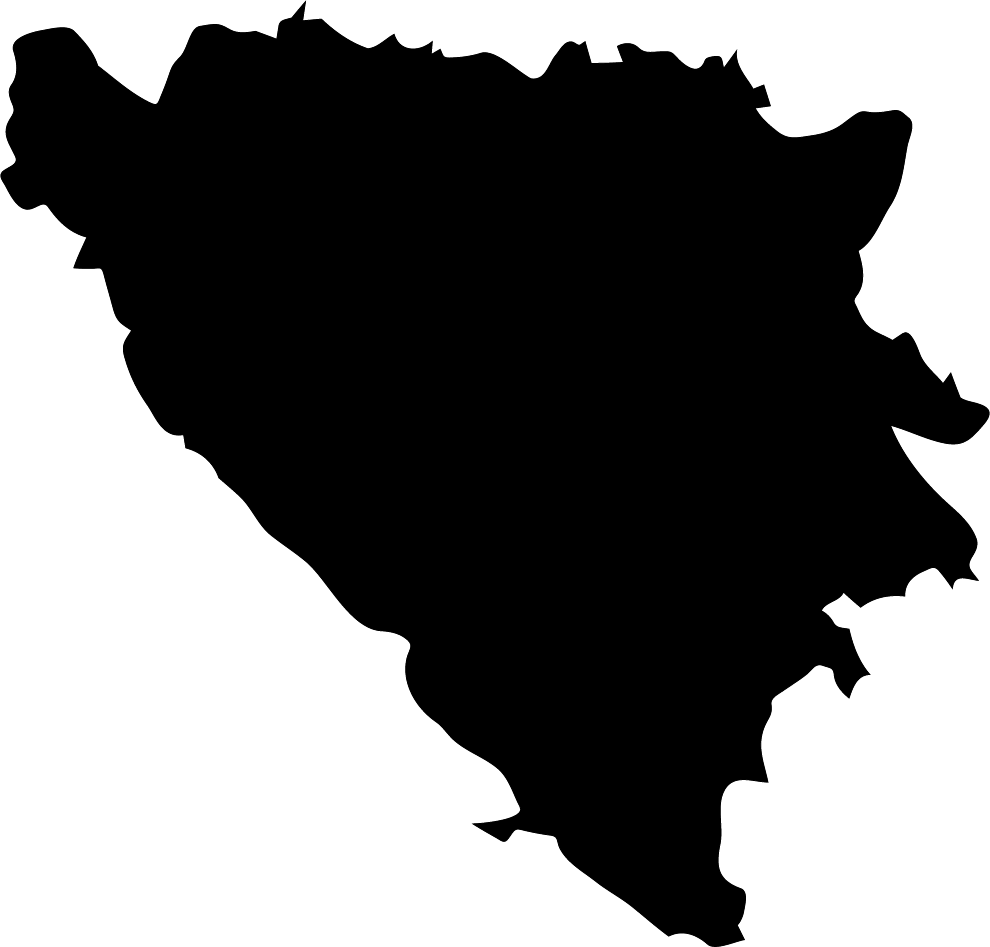
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Overall Score: 58

Cambodia
Overall Score: 58
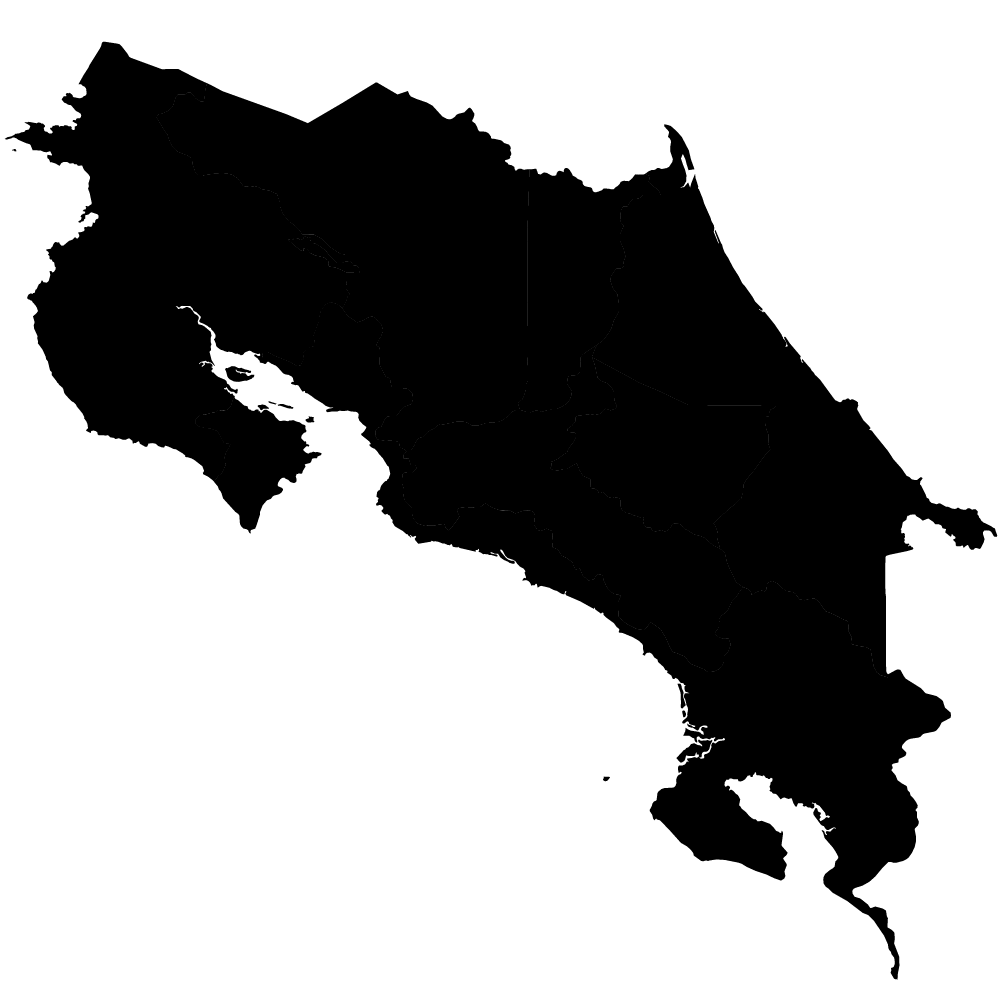
Costa Rica
Overall Score: 58
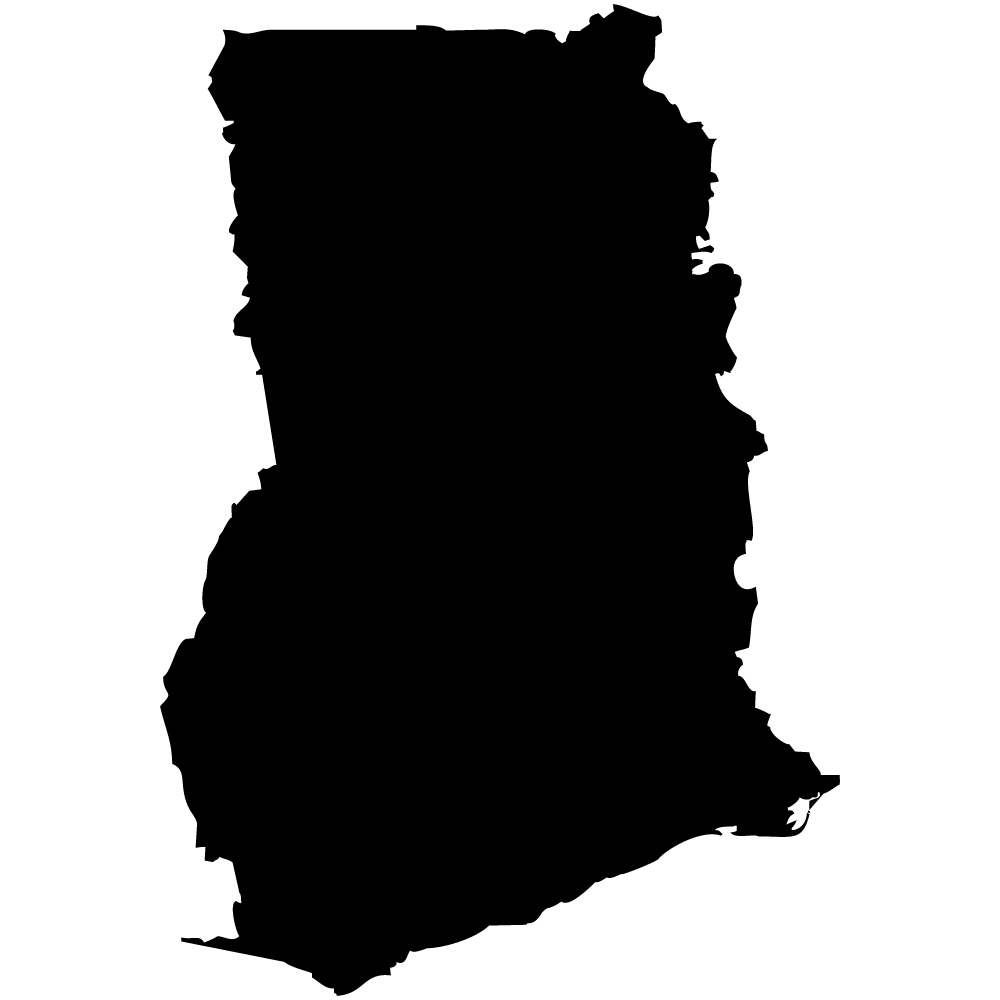
Ghana
Overall Score: 58
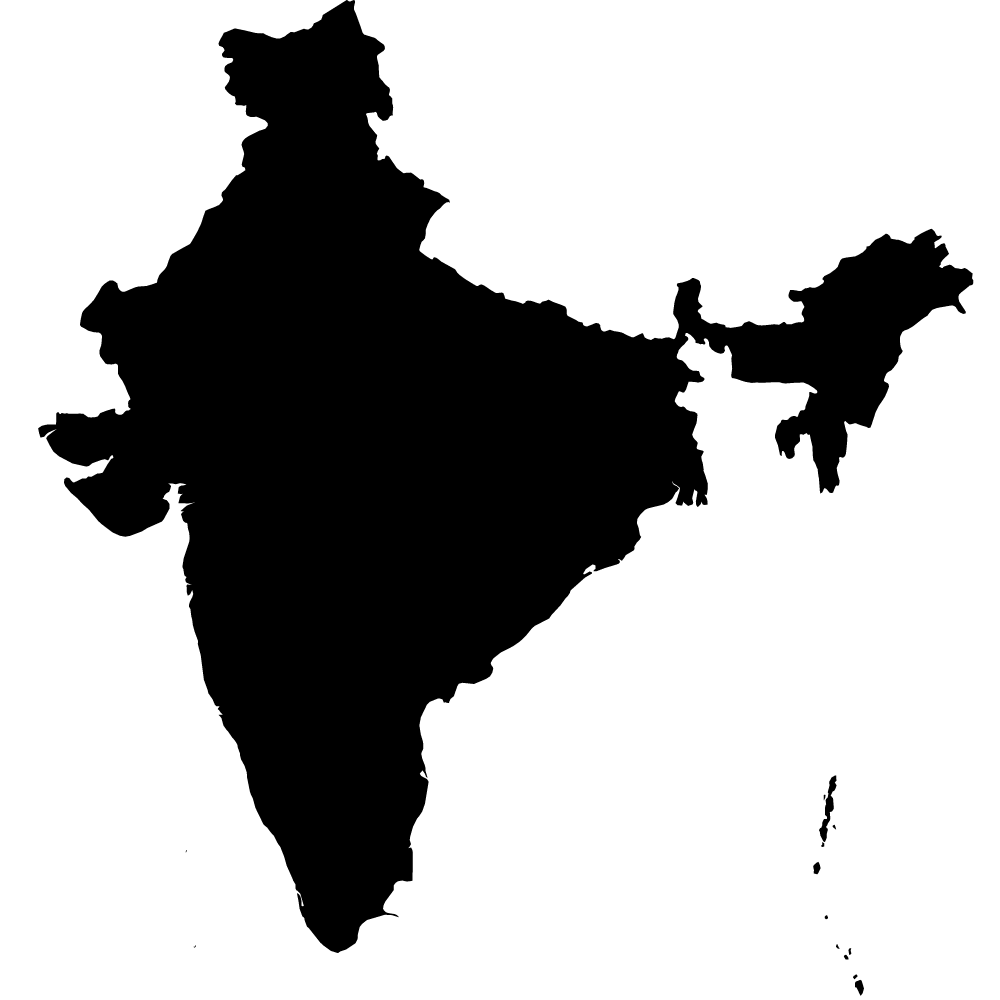
India
Overall Score: 58
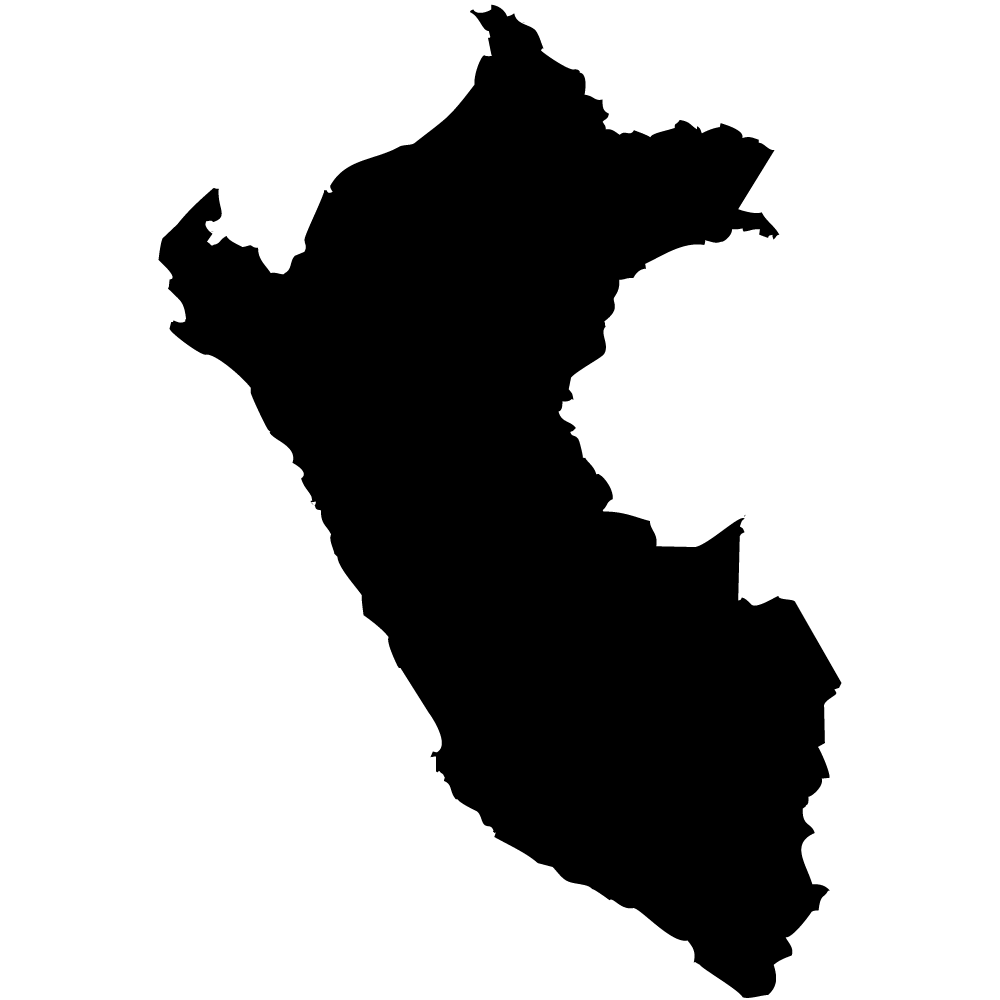
Peru
Overall Score: 59
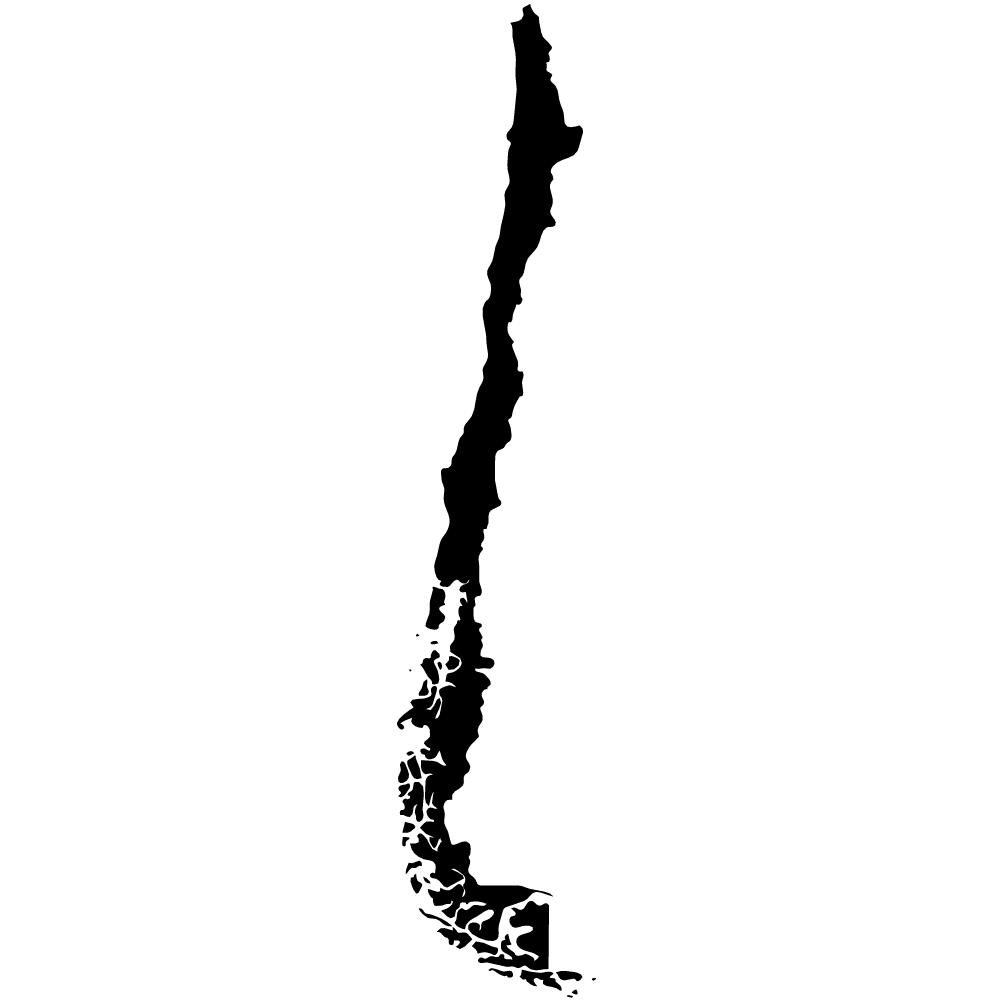

Chile
Overall Score: 60
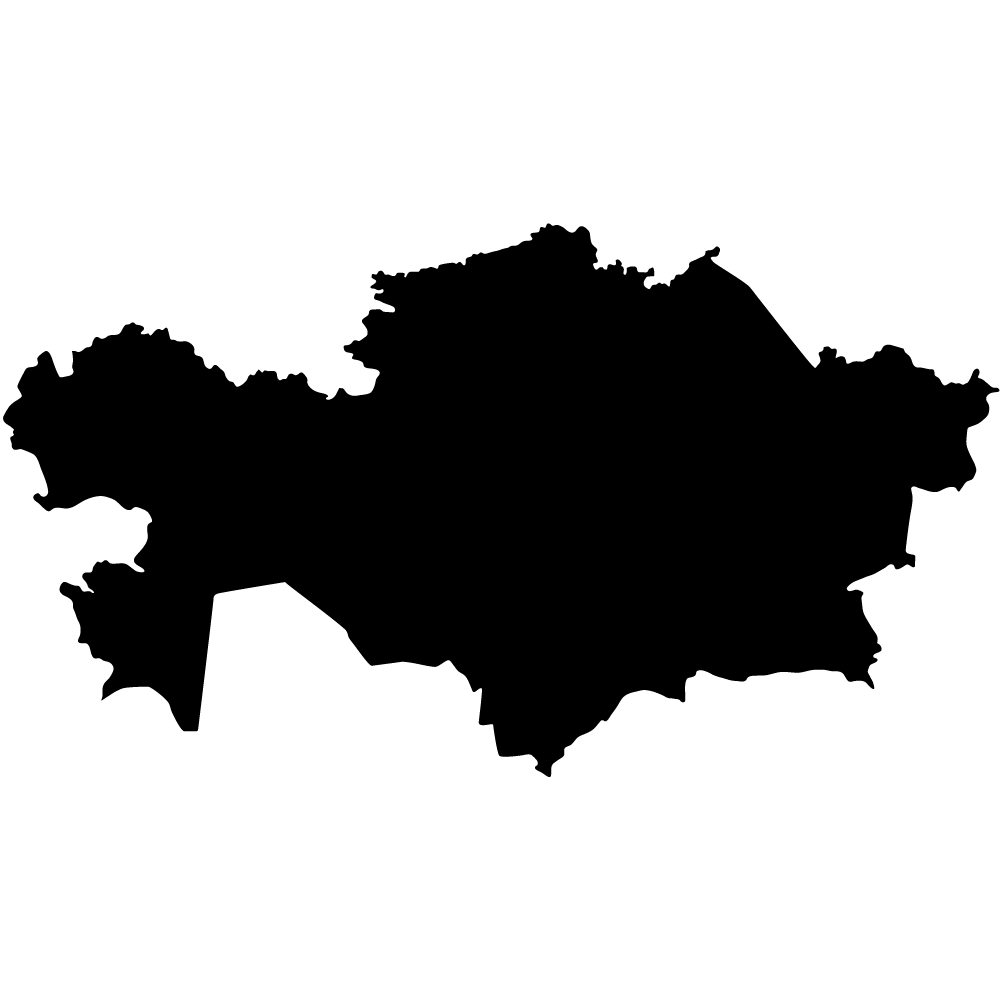

Kazakhstan
Overall Score: 60

Republic of Korea
Overall Score: 60

Lebanon
Overall Score: 60
Nigeria
Overall Score: 60
Philippines
Overall Score: 60

Venezuela
Overall Score: 60

Sweden
Overall Score: 61

El Salvador
Overall Score: 62
Poland
Overall Score: 62

Egypt
Overall Score: 63

South Africa
Overall Score: 64

Fiji
Overall Score: 65
Brazil
Overall Score: 66
Ecuador
Overall Score: 66
Uruguay
Overall Score: 66
Guatemala
Overall Score: 67
Iraq
Overall Score: 67
Mozambique
Overall Score: 67

Czech Republic
Overall Score: 68
Madagascar
Overall Score: 69
Bolivia
Overall Score: 70
Germany
Overall Score: 70

Honduras
Overall Score: 70
Lao PDR
Overall Score: 70
Paraguay
Overall Score: 70
Bangladesh
Overall Score: 72

Türkiye
Overall Score: 72

Bulgaria
Overall Score: 73

China
Overall Score: 73
Argentina
Overall Score: 74
Italy
Overall Score: 75
Malaysia
Overall Score: 76
Zambia
Overall Score: 77
Colombia
Overall Score: 78
Tanzania
Overall Score: 79

Romania
Overall Score: 80
United States of America
Overall Score: 80
Cameroon
Overall Score: 81

Jordan
Overall Score: 82
Georgia
Overall Score: 83
Indonesia
Overall Score: 84

Japan
Overall Score: 88

Switzerland
Overall Score: 95

Dominican Republic
Overall Score: 100